
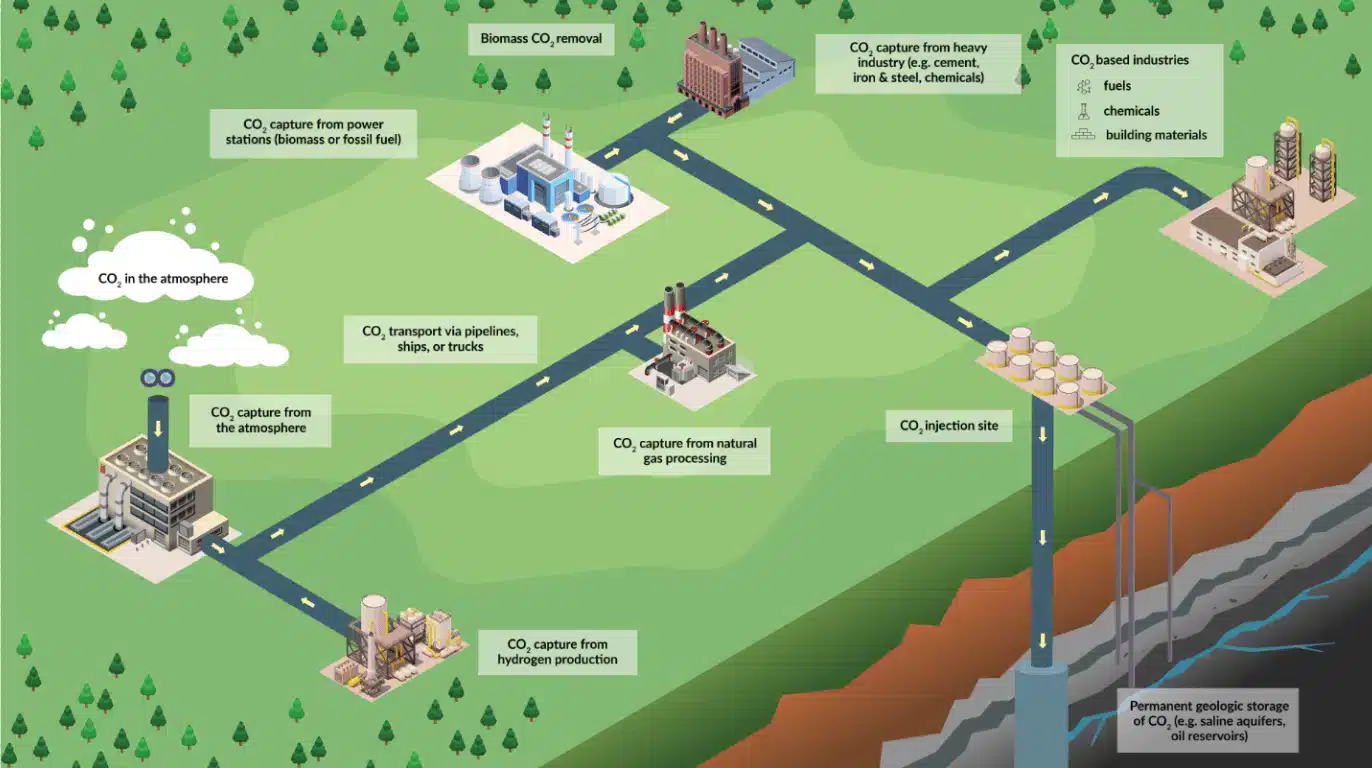
The construction industry indeed faces a colossal challenge with carbon emissions, particularly in cement production. However, there is hope with Heidelberg Materials' Edmonton CCUS Project, which is poised to be the world's first full-scale carbon capture marvel in the cement world. Partnering with industry titans like Technip Energies and Shell, this project aims to capture a staggering 1 million tons of CO2 annually, equivalent to removing 300,000 cars from the road!
>> RELATED: Heidelberg Materials North America Announces Latest Step in Edmonton CCUS Project
Let's delve deep into Heidelberg's ambitious plan, exploring the project's details, the crucial role of carbon capture in decarbonizing cement, and ultimately, unveiling how this initiative paves the way for a net-zero future in construction.
The Edmonton CCUS Project: Heidelberg's Two-Stage Quest
“We are excited to take this latest step in our journey to produce the world’s first net-zero cement,” said Joerg Nixdorf, Vice President Cement Operations, Northwest Region for Heidelberg Materials North America. “With each milestone we come closer to realizing our vision of leading the decarbonization of the cement industry.”
Heidelberg Materials' Edmonton CCUS Project, aiming for net-zero cement production, employs a two-stage approach. In stage one, Technip Energies, a leading engineering player, was selected to provide the crucial front-end engineering and design (FEED) for the carbon capture technology. Leveraging the Shell CANSOLV® CO2 capture system, a cutting-edge solution employing regenerable amine technology, as the foundation for this FEED study, paves the way for stage two: selecting the contractor to bring this ambitious decarbonization dream to life.
Technip's Carbon Capture Game-Changer
Technip Energies steps onto the Edmonton CCUS Project stage with a powerful weapon: the Shell CANSOLV® CO2 capture system. Its secret lies in regenerable amine technology, a cutting-edge approach capturing CO2 with high efficiency and low energy consumption. Compared to traditional methods, it's like comparing a steam engine to a sleek electric car. This marvel translates to real-world impact.
"Partnering with Heidelberg Materials North America to provide the FEED of this groundbreaking project in Canada is a significant step towards decarbonization," said Christophe Malaurie, SVP Decarbonization Solutions for Technip Energies. "Leveraging our carbon capture solution powered by the Shell CANSOLV® CO2 capture system, we are committed to supporting the decarbonization of the cement industry and Heidelberg towards the production of net-zero cement."
Heidelberg's project, armed with this technology, aims to capture a million tons of CO2 annually – a game-changer for the emissions-heavy cement industry. It establishes a new standard, showcasing the practicality of industrial decarbonization, leading to a cleaner future, not only for cement but also for numerous industries facing emissions challenges. This goes beyond mere carbon capture; it envisions a future where sustainable manufacturing is the norm.
Environmental Impact and Net-Zero Cement Production
Imagine a cement plant leaving no carbon footprint. Heidelberg Materials' Edmonton project dares to make it real, aiming for net-zero production. This means capturing and storing a staggering 1 million tons of CO2 annually – equivalent to removing 300,000 cars from the road forever. The impact? Monumental.
Firstly, it cleans the air we breathe. Capturing this much CO2 is like planting 40 million trees every year, a significant dent in greenhouse gas emissions that contribute to climate change. This project sets a powerful precedent, proving that even heavy industries like cement can embrace sustainable practices.
Heidelberg's initiative is more than just a local win; it's a beacon for the entire industry. It demonstrates the feasibility of net-zero cement production, paving the way for a future where construction leaves a lighter footprint on our planet. This is not just about bricks and mortar – it's about building a more sustainable future, one green ton at a time.
Counting the Cost of a Greener Cement Future

Capturing carbon is indeed a noble pursuit, but the associated costs raise concerns. The integration of CCUS technology, such as Heidelberg's Edmonton project, entails significant initial investments and ongoing operational expenses. The question of its economic viability hinges on finding a delicate balance.
While the upfront costs are substantial, the potential operational savings resulting from reduced energy consumption are promising. Moreover, the sale of captured CO2 could create new revenue streams. However, these uncertainties underscore the critical importance of government support.
Policy incentives and funding, like those expected for the Edmonton project, can help bridge the economic gap and expedite widespread adoption. Ultimately, the expense of inaction on climate change far surpasses the investment in CCUS. Heidelberg's project lays the groundwork for a more sustainable future, but without supportive policies, the path forward may remain financially precarious.
Despite the remaining challenges, Heidelberg's Edmonton CCUS Project is a beacon of hope, demonstrating that net-zero cement production is no longer just a dream but a tangible reality. Its success relies on collaboration, innovation, and responsible investment, paving the way for a cleaner future where construction thrives in harmony with our planet.
Subscribe to the newsletter
Daily decarbonization data and news delivered to your inbox
Follow the money flow of climate, technology, and energy investments to uncover new opportunities and jobs.
Companies
Latest issues
-
Sustaera's 3rd-Gen DAC Could Crack the $100/Ton Barrier
Inside This Issue 🧪 Sustaera's 3rd-Gen DAC Could Crack The $100/Ton Barrier ⚠️ Middle East Conflict Threatens To Derail The Region's Carbon Capture Boom 🌿 Svante And Integrated Packaging Company A...
-
PJM's AI Power Crisis Just Got a 250MW Hydrogen Answer
Inside This Issue ⚡ Plug Power Plans Hydrogen Offering in Top US Power-Grid Auction 🪨 Underground CO2 Storage, X-Rays Reveal Carbon Capture Capacity of Volcanic Rocks 🍁 Swiss Carbon Capture Compan...
-
One Montana Site Could Supply Half of North America's SAF
Inside This Issue ✈️ Montana's $1.44B Bet on Aviation Fuel Enters Final Stretch 🌍 Carbon Removal Coalition Forms With Goal of Attracting $100-Million in Project Investments 🤝 Prime Minister Carney...
Company Announcements
-
CHARBONE CORPORATION (TSXV: CH; OTCQB: CHHYF; FSE: K47) ("CHARBONE" or the "Company"), a North American producer and distributor specializing in clean Ultra High Purity ("UHP") hydrogen and strateg...
-
Axens Signs Memorandum Of Understanding With Airbus On SAF Development
Axens has signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with Airbus to strengthen their cooperation in the development and deployment of Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF), a key pillar for decarbonizing...
-
Renewable-Powered Technology Converts Carbon Dioxide Into Key Chemical
Catalyst Design Increases Efficiency, Turning Captured CO₂ Into High-Purity Ethylene For Plastics, Packaging The Problem Most of the world’s ethylene is produced from fossil fuels, generating lar...
-
Next Hydrogen Secures Contracts Totaling $3.75 Million for Specialized Nuclear Application
MISSISSAUGA, Ontario -- Next Hydrogen Solutions Inc. (“Next Hydrogen” or the “Company”) is pleased to announce that it has been awarded two contracts with a combined value of approximately $3.75 mi...

